What Are the Characteristics of the Sahara Desert?
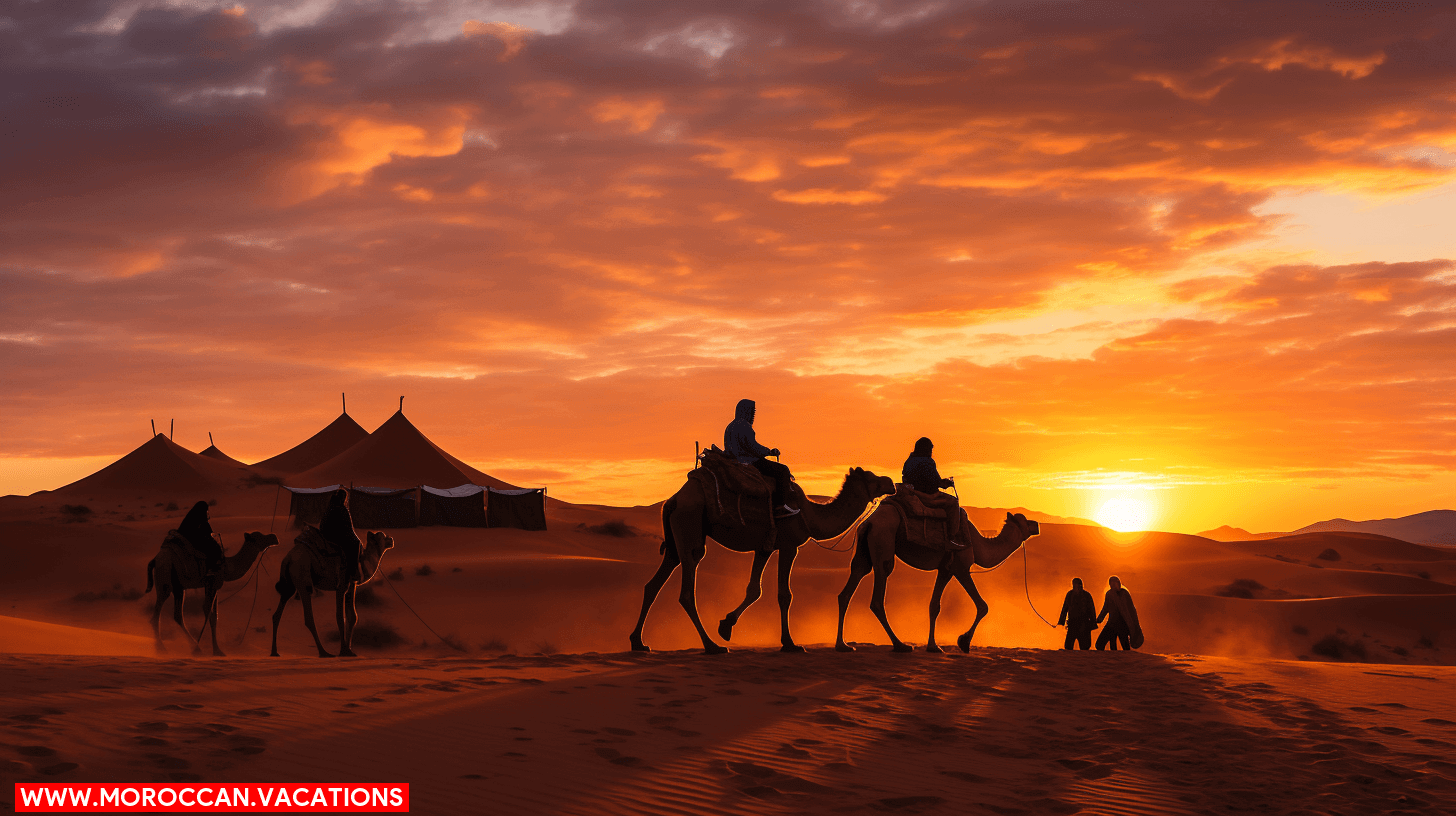

You’re standing at the helm of vastness, ready to chart a course through the golden sea of dunes. The Sahara desert, Earth’s largest hot desert, calls out to your wandering spirit. Stretching across North Africa, it’s an expansive canvas, painting Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, Mauritania, Mali, Niger, Chad, and Sudan with hues of solitude and endurance. This desert isn’t just a geographical wonder; it’s a crucible of life, where resilient flora and fauna defy the harsh climate. Your quest for freedom finds resonance in the Sahara’s boundless horizons, where the sky kisses the sand, and the winds whisper tales of ancient caravans. As you traverse this arid expanse, remember the Sahara is more than a place—it’s the embodiment of liberty, a testament to the Earth’s wild heart.
You’ll find that the Sahara Desert’s climate is characterized by extreme diurnal temperature variations, with sweltering days and frigid nights. Its unique ecosystem, including both flora and fauna, has adapted to the arid conditions and stark landscapes, which are punctuated by vital oases that support life. As the largest hot desert, the Sahara’s physical geography is marked by expansive dunes, rocky plateaus, and the occasional mountain peak.
Climate and Temperature Variations in the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert’s climate is characterized by extreme temperature fluctuations, with scorching days and chilly nights. Desert precipitation is scarce, leading to arid conditions year-round. You’ll find that sandstorms frequency intensifies these harsh conditions, reducing visibility and transforming the landscape. Nocturnal temperature drops are drastic, often plummeting after sunset due to the low humidity levels that do not retain the day’s heat.
- Factors influencing Sahara’s climate:
- Solar radiation: High levels contribute to daytime heat.
- Humidity levels: Generally low, causing significant diurnal temperature variation.
Microclimate diversity within the Sahara creates pockets where life defies the odds. Here, you breathe in freedom, witnessing nature’s resilience in the face of adversity. These microclimates offer respite, showcasing an ecosystem’s ability to adapt and thrive.
Unique Flora and Fauna of the Sahara Desert
Amidst the sea of sand, you’ll discover the Sahara Desert’s unique flora and fauna, which have remarkably adapted to its harsh environment. Desert vegetation has evolved to minimize water loss, using deep root systems and reduced leaf surfaces. Date palm cultivation thrives near oases, providing sustenance and shade.
Carnivores like the elusive Saharan cheetah showcase physiological and behavioral adaptations for survival, including a lean physique for efficient heat dissipation. The nimble sand cats, with their insulated paws, navigate the scorching sands, preying on small rodents. Desert fox adaptations, such as large ears for thermoregulation, demonstrate nature’s ingenuity.
Scarab beetles, integral to the nutrient cycle, thrive by consuming detritus. Each species signifies the Sahara’s complex ecosystem, embodying resilience and freedom in a boundless desert landscape.
Largest Hot Desert in the World: The Sahara
In exploring the Sahara Desert, you’ll encounter the world’s largest hot desert, characterized by vast dune fields, rocky plateaus, and minimal rainfall.
- Saharan sandstorms
- Impact: Abrasive and disorienting, these sandstorms shape the desert’s dynamic landscape.
- Emotion: They evoke a sense of awe and respect for the desert’s untamed nature.
- Desertification threats
- Analysis: Accelerated by human activities, desertification encroaches upon the freedom of both the environment and local communities.
- Concern: Calls for sustainable practices to preserve the desert’s fragile ecosystem.
The Sahara boasts significant mineral resources, promising solar energy potential, and historic trade routes that have connected cultures for centuries. Yet, amidst these valuable assets, cultural festivals flourish, celebrating the indomitable spirit of freedom that the Sahara’s vastness inspires.
How are Oases Essential to Life in the Sahara Desert?
As you traverse the arid expanse of the Sahara, oases become crucial lifelines, offering respite and sustenance in a landscape otherwise devoid of water. These isolated green sanctuaries are underpinned by subterranean aquifers or natural springs, enabling desert agriculture through irrigation. Plants, animals, and humans have adapted intricate survival strategies around these water sources. Oasis ecosystems, often complex and fragile, are biodiversity hotspots that balance the harsh desert climate.
Strategically, oases have historically anchored trade routes, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural rituals. They’re not just waterholes but nodes of freedom, where travelers and traders could determine new paths or rest before venturing into the unknown. In essence, oases are the lifeblood of the Sahara, making existence and navigation possible in this vast desert.
Physical Features: Dunes, Valleys, and Peaks in the Sahara
You’ll find the Sahara’s landscape dominated by vast dunes, rugged valleys, and towering peaks, each contributing to the desert’s unique and diverse topography. The dunes, known as ergs, form extensive sand seas that shift with the wind patterns, sculpting an ever-changing canvas of natural beauty. Amidst these seas, you’ll encounter:
- Rock formations:
- Stark and majestic, they rise from the desert pavements, a testament to the Sahara’s ancient geological past.
- These formations are often rich in mineral wealth, hinting at untapped freedom beneath the surface.
The valleys and peaks offer dramatic vistas for star gazing, unobstructed by the trappings of modernity. Here, you’re free to explore the Sahara’s wild heart, where each grain of sand tells a story of time’s relentless march.
Who Inhabits the Sahara Desert?
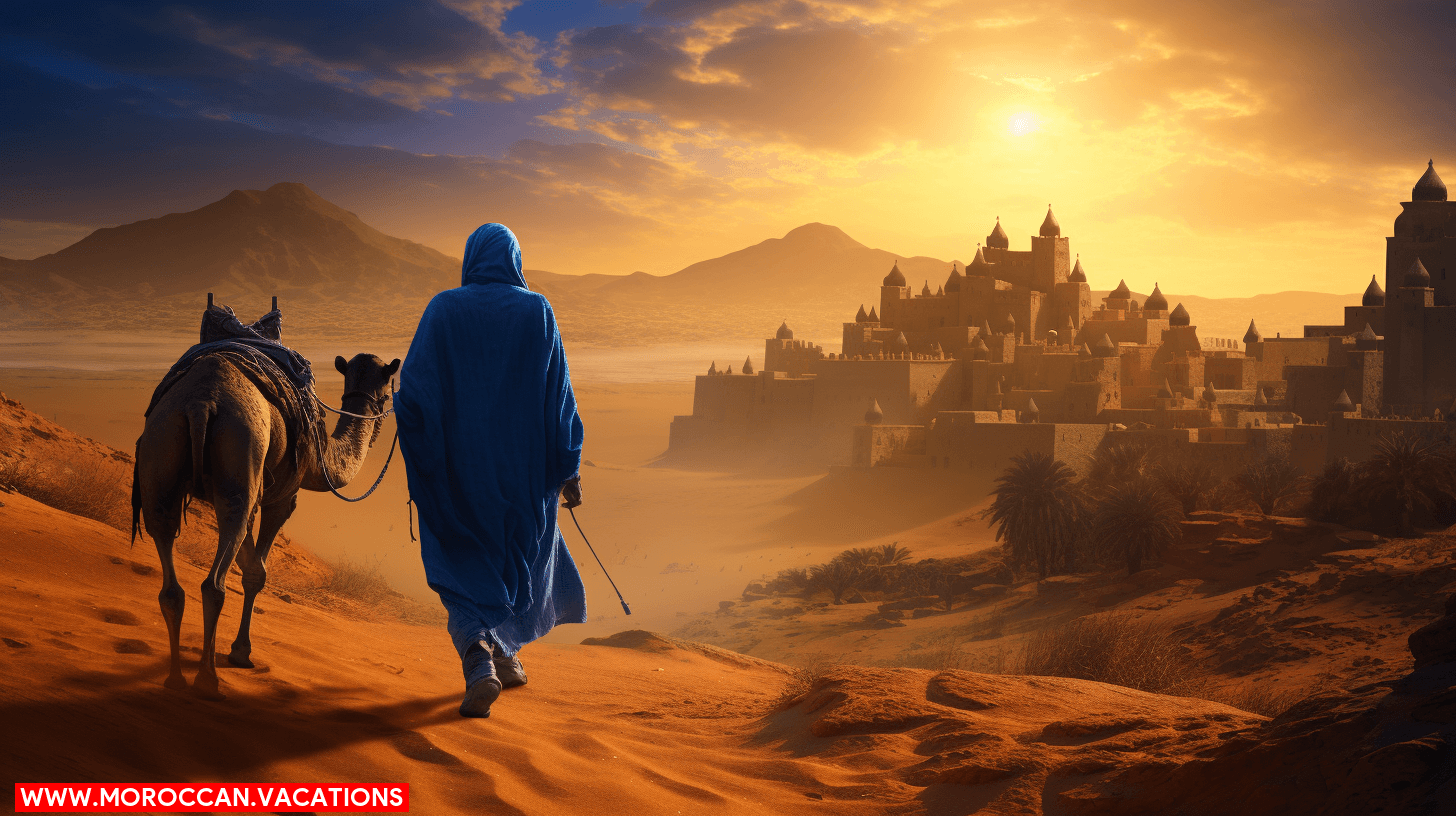

You’ll find that the vast expanse of the Sahara Desert is not devoid of human life; rather, it hosts nomadic groups like the Berbers, who have adapted their lifestyles to the harsh environment. The dromedary camel, often referred to as the “ship of the desert,” is a key species for inhabitants, providing transportation, milk, and meat, crucial for survival in this arid terrain. Moreover, the desert conceals remnants of ancient civilizations, offering insight into the historical human occupation that once thrived before the Sahara’s climate shifted to its current state.
Life of Nomads and Berbers in the Sahara Desert
Venturing into the vast expanses of the Sahara Desert, you’ll encounter the resilient nomadic tribes and Berber communities that have made this harsh landscape their home for centuries.
- Nomadic Traditions and Berber Culture
- Berber Music: Emotive melodies that echo the winds of freedom across the dunes.
- Tribal Languages: Linguistic threads weaving through the fabric of the desert society.
The nomads’ profound understanding of this environment is reflected in their adaptive strategies. Their life is a testament to human resilience; they’ve harnessed skills like sand surfing to navigate the dunes, turning an arduous journey into an expression of liberty. Desert crafts exhibit both artistic and functional elements, essential for survival. The caravan trade remains a lifeline, as it facilitates not just the exchange of goods but also cultural and informational flows across the Sahara.
Camel: The Ship of the Sahara Desert
Among the many inhabitants of the Sahara Desert, you’ll often find herds of camels, the indispensable companions to the region’s nomads. These adept creatures have evolved for arid conditions, showing remarkable adaptations for water conservation and desert navigation. Their unique physiological traits enable them to endure long periods without drinking, efficiently storing water in their bodies. Camel breeding is a sophisticated practice, honed over centuries, aiming to enhance traits that facilitate sand surfing across dunes and endurance under extreme heat.
Camels also bear deep cultural symbolism, woven into the fabric of Saharan life. They’re featured in traditional medicine, believed to possess curative properties. For you, seeking autonomy in knowledge, understanding the symbiosis between camels and humans in the Sahara is key to grasping the desert’s complex ecosystem.
Exploring the Ancient Civilizations of the Sahara
Several ancient civilizations once thrived in the vast expanse of the Sahara Desert, shaping its history and culture. As you explore the remnants of these communities, you uncover:
- Neolithic remnants
- Evidence of pastoral nomadism
- Tools and pottery fragments symbolizing self-reliance and resilience
- Rock paintings
- Depictions of a greener Sahara, teeming with life
- Artistic expressions of freedom and identity
These artifacts, discovered through meticulous desert archaeology, narrate stories of societies entwined with the land. Ancient trade routes once connected caravan cities, fostering exchange and the spread of ideas. Saharan art, etched into stone, reveals a vibrant culture unbounded by the harsh desert climes. This evidence of past inhabitants conveys a message of adaptation and endurance in the quest for autonomy amidst a challenging and ever-changing landscape.
Impact of Modern Settlements in the Sahara Desert
You’ll often find that the Sahara Desert, despite its harsh environment, is home to various modern settlements and nomadic tribes. Desert urbanization, although sparse, presents unique challenges such as water scarcity and habitat disruption. These settlements often grapple with agricultural challenges due to arid soils and sand encroachment that threatens to bury infrastructure. However, the vast, sun-soaked expanses offer significant renewable energy potential.
| Aspect | Impact on Settlements | Scientific Note |
| Desert Urbanization | Expansion into arid regions | Requires sustainable water sourcing |
| Water Scarcity | Limits population growth | Necessitates efficient water usage |
| Habitat Disruption | Alters indigenous ecosystems | Demands ecological impact assessments |
| Sand Encroachment | Threat to existing structures | Calls for innovative architectural designs |
| Agricultural Challenges | Constrained food production | Invokes development of drought-resistant crops |
| Renewable Energy Potential | Economic and power autonomy | Exploits consistent solar irradiance |
These elements underscore the delicate balance between human habitation and the desert’s natural state, urging a pursuit of harmony with the environment.
Fascinating Facts About the Sahara Desert


You may find the enigmatic mysteries and folklore surrounding the Sahara Desert as intriguing as its vast, arid expanses; these tales offer a rich tapestry of the region’s cultural heritage. The Sahara’s immense geographical and historical significance has shaped human civilizations for millennia, influencing trade routes, settlement patterns, and even warfare. Crucially, this desert plays a pivotal role in climate change and global ecosystems, affecting atmospheric conditions and biotic communities far beyond its own borders.
Enigmatic Mysteries and Folklore of the Sahara Desert
Amidst the vast expanse of the Sahara Desert, numerous legends and enigmatic sites await your discovery. The desert’s lore is as boundless as its sands, encompassing:
- Desert legends
- The tale of Tanezrouft, a land so desolate even desert spirits dare not linger.
- Sand mysteries
- Cryptic Nazca-like lines, visible only from above, their creators and purposes lost to time.
- Mirage tales
- Stories of ghostly cities appearing in the heat-haze.
- Caravan secrets
- Ancient routes laden with histories of forgotten trades.
- Desert spirits
- Jinn, said to roam freely, whispering to the unwary traveler.
- Ancient myths
- The lost civilization of Atlantis, rumored to lie beneath these shifting dunes.
Each element is a piece of a puzzle, hinting at a freedom that the desert holds—secrets guarded by time, awaiting the tenacious seeker.
Geographical and Historical Significance of the Sahara
Exploring its geographical and historical significance, one discovers that the Sahara Desert, the largest hot desert in the world, has shaped civilizations and trade routes for millennia. Spanning approximately 9.2 million square kilometers, Sahara’s size influences regional climate. Its expansion, through desertification causes such as climate variations and unsustainable land use, poses challenges to desert agriculture.
Ancient trade routes once bustled across this arid expanse, connecting empires and facilitating the exchange of goods and culture. The Sahara is not devoid of wealth; it sits atop substantial mineral resources, including phosphates and iron ore, driving modern economic interests.
Moreover, archaeological sites pepper the landscape, offering a window into prehistoric human life. Understanding these elements is key to appreciating the Sahara’s role in past, present, and future human endeavors.
Sahara’s Role in Climate Change and Global Ecosystems
The Sahara Desert plays a pivotal role in global climate patterns, affecting ecosystems far beyond its sandy borders.
- Desertification process:
- Expands the Sahara’s reach, threatening livelihoods and freedom to thrive.
- Induces sand encroachment, impeding agriculture and natural habitats.
- Climate Impact:
- Wind erosion and dust storms transport vital minerals but also degrade soil quality.
- Carbon storage capacity is compromised, exacerbating climate change.
This arid expanse is not only a source of concern. It harbors immense solar potential, offering a beacon of freedom for renewable energy exploitation. The Sahara’s influence is profound, and understanding its mechanisms is essential to mitigating climate change and securing ecological liberty worldwide.
Human-Environment Interactions in the Sahara Desert
Navigating the Sahara Desert, you’ll encounter a dynamic human-environment interplay where communities have adapted to extreme conditions for millennia. The stark landscape reveals a history of desert agriculture, persisting despite water scarcity. Sand encroachment threatens existing oases, yet these resilient settlements ingeniously manage resources.
The Sahara’s vastness holds untapped solar energy potential, promising freedom from fossil fuels. Mineral resources, buried beneath the dunes, beckon industrial opportunities. However, frequent dust storms pose challenges, affecting air quality and climate far beyond the Sahara’s bounds.
Here’s a scientific snapshot:
| Factor | Impact on Human-Environment Interaction |
| Desert Agriculture | Utilizes ancient water-conservation techniques |
| Water Scarcity | Drives innovation in resource management |
| Dust Storms | Influences global climate patterns |
Understanding these elements is crucial for a sustainable coexistence with this formidable desert.
Adventurous Treks and Expeditions in the Sahara
You’ll often find that embarking on a trek across the Sahara Desert offers a unique blend of challenge and awe-inspiring vistas. The Sahara’s vast expanse beckons with an array of activities:
- Desert safaris
- Traverse the rolling dunes in 4×4 vehicles, equipped to tackle the off roading challenges inherent to the sandy terrain.
- Experience the freedom of the desert, unhindered by the confines of urban landscapes.
- Nocturnal marvels
- Star gazing: Peer into the cosmos through the clear Saharan sky, a window to the universe.
- Moonlit walks: Navigate the tranquil dunes under a silver glow, the silence punctuated only by the whisper of shifting sand.
Sandboarding adventures and desert camping immerse you in the Sahara’s elemental beauty, highlighting the desert’s multifaceted character.
Introducing Ayoub Karbachi, a brilliant wordsmith and curator of the Moroccan Vacations website. Prepare to immerse yourself in mesmerizing narratives and extraordinary moments, as he unveils the allure of Morocco's captivating destinations like never before.
Related Articles
What Animals Live in the Sahara Desert
Types of Animals Found in the Sahara Desert Photo by: @https://owlcation.com/stem/sahara-desert-animals Imagine yourself tracking the majestic dromedary camel across the vast, sandy dunes of the Sahara Desert. As you embrace the spirit of adventure, you're not alone...
What Is a Riad in Morocco?
Discover the allure of a Riad in Morocco with our comprehensive guide. Uncover the essence of these traditional Moroccan homes, their unique architecture, and the cultural significance they hold.
What Religion Is Practiced in Morocco?
Explore the rich tapestry of religious diversity in Morocco. Discover the predominant religion practiced in Morocco, its cultural significance, and the harmonious coexistence of various faiths. Uncover the spiritual mosaic that defines Morocco’s unique religious landscape.



