Types of Animals Found in the Sahara Desert
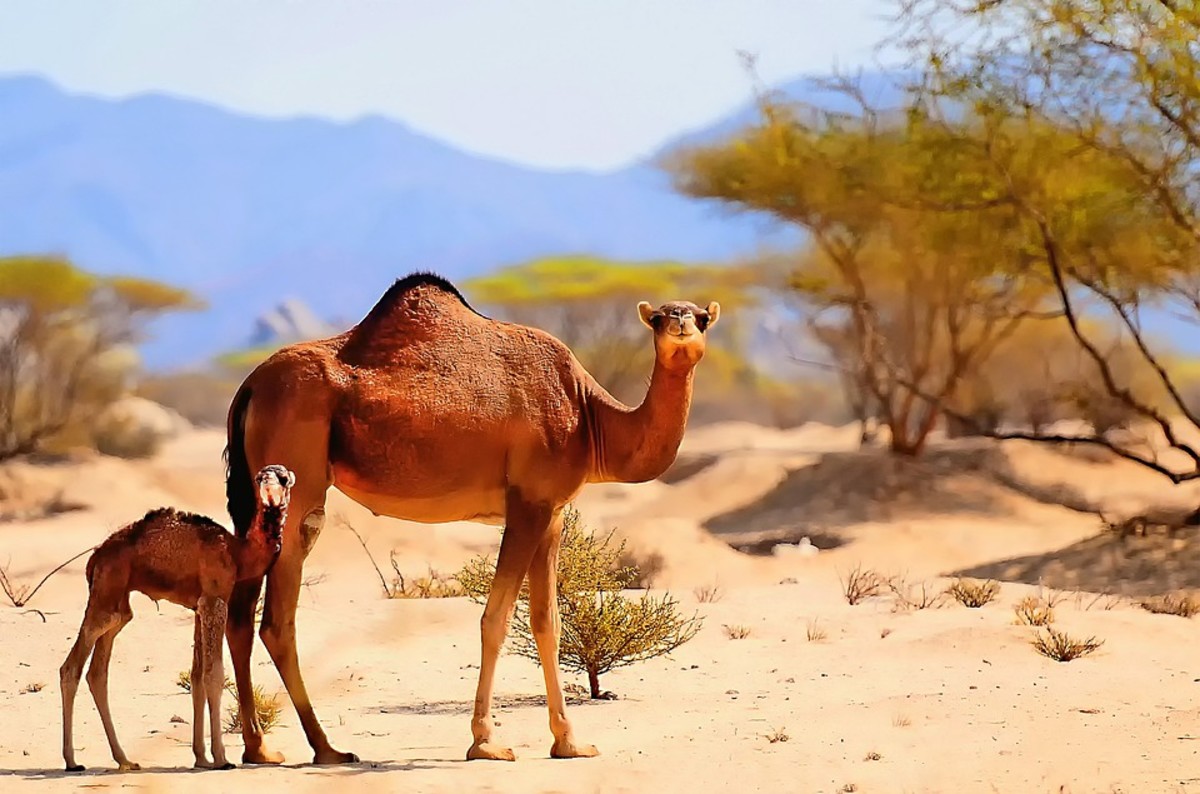


Photo by: @https://owlcation.com/stem/sahara-desert-animals
Imagine yourself tracking the majestic dromedary camel across the vast, sandy dunes of the Sahara Desert. As you embrace the spirit of adventure, you’re not alone in your quest for freedom. This desert is teeming with life, defying the harsh conditions. You’ll find resilient animals, each uniquely adapted to the extreme climate. The fennec fox, with its oversized ears, dissipates heat and listens for prey beneath the sand. You may spot the elusive Saharan cheetah, a master of stealth and speed, or the hardy desert antelope, navigating the scarcity with grace. Your journey through the Sahara is a testament to the freedom found in coexistence with these remarkable creatures, each playing a vital role in the ecosystem. As you traverse this open landscape, remember the significance of every animal you encounter, for they are the true navigators of liberty in this boundless desert.
As you explore the Sahara Desert’s biodiversity, you’ll find camels, renowned for their adaptation to arid conditions, serving as a keystone species. You’ll also encounter a variety of mammals such as the fennec fox, alongside a spectrum of specialized reptiles and insects, each uniquely suited to the extreme desert climate. Furthermore, the presence of ostriches and other avian species illustrates the broad ecological niche coverage within this harsh environment, despite the growing concern for endangered species that struggle to survive here.
Camels in the Sahara Desert
Among the myriad species that have adapted to the harsh conditions of the Sahara Desert, you’ll find the resilient camel as a signature inhabitant. Camel breeds, notably the dromedary, have evolved to thrive amidst the arid landscape. Their diets are varied, efficiently converting desert vegetation into energy. Debunking water storage myths, camels’ humps actually store fat, which can be metabolized when resources are scarce. Camel domestication has been pivotal to human survival in these expanses; they’re integral to the cultural fabric, having served caravan roles, transporting goods and people across vast, unforgiving terrains. Analyzing their adaptation strategies offers insights into nature’s ingenuity, ensuring these creatures continue to symbolize the spirit of freedom that the Sahara’s endless horizons represent.
Fennec Fox and Other Mammals
You’ll also encounter the fennec fox, a small nocturnal mammal, distinguished by its oversized ears, which roam the dunes of the Sahara. Those ears aren’t just for show; they’re crucial for ear thermoregulation, dissipating heat to keep the fox cool in the sweltering desert climate. As you analyze this creature’s behavior, you’ll notice its nocturnal activity is a strategic adaptation to avoid the daytime heat.
Their desert diet is varied, opportunistic, and includes plants, insects, and small animals, showcasing their adaptability. When it comes to sand digging, these foxes are experts, creating extensive burrows for shelter and to escape predators. Even their mating rituals are adapted to their environment, occurring once a year, ensuring their offspring are born during cooler months.
Reptiles and Insects Native to the Sahara Desert
Shifting focus to the cold-blooded inhabitants of the Sahara, you’ll find a diverse array of reptiles and insects that have mastered the art of desert survival. Their adaptations are a testament to nature’s ingenuity in the face of extreme conditions.
- Sahara geckos: Nocturnal creatures that avoid the daytime heat, exhibiting exceptional camouflage against the desert backdrop.
- Scorpion venom: A powerful tool for predation and defense, evolved in species like the deathstalker, to subdue prey and deter threats.
- Desert locusts: Capable of forming massive swarms that traverse vast distances, these insects are both fascinating and formidable in their impact on the ecosystem.
- Antlion pits: Ingenious traps set by the larvae of antlions, designed to capture unsuspecting insects in a sandy grave.
The resilience of these species, such as the spiny-tailed lizards, underscores your understanding of freedom in life’s unyielding quest for survival.
Endangered Species Adapted to the Harsh Environment
As you delve deeper into the Sahara’s wildlife, consider the dama gazelle, a majestic mammal now on the brink of extinction due to its unforgiving desert home. Desertification impacts their habitat, reducing available food and water sources, which in turn, threatens their survival. You’ll find that climate change exacerbates these conditions, leading to even more habitat loss. Poaching threats loom large as well, with the dama gazelle being a target for illegal wildlife trade, further decimating their numbers.
Genetic diversity is critical for species adaptation and resilience; however, with dwindling populations, the genetic pool of the dama gazelle narrows, compromising their ability to adapt to environmental changes. Hence, their plight in the Sahara is a stark reminder of the intricate balance between wildlife and their ecosystems.
Ostriches and Other Birds in the Sahara Desert
Amid the relentless heat of the day, ostriches—the world’s largest birds—thrive in the Sahara Desert alongside a surprisingly diverse array of avian species. Your understanding of their survival tactics begins with examining their:
- Ostrich Diet: Primarily consisting of plant matter, insects, and lizards, their diet is perfectly attuned to the sparse offerings of the desert.
- Bird Migration: Many species exhibit seasonal migration patterns, strategically relocating to exploit temporary abundance.
- Avian Predators: Raptors, such as the Lanner falcon, utilize keen eyesight and speed to hunt in the arid landscape.
- Nesting Habits: Ground-nesting birds camouflage their nests, while others may use cliff faces to evade terrestrial threats.
- Feather Adaptation: Ostriches, and other birds, have feathers adapted for temperature regulation, crucial for enduring the extreme desert climate.
Unique Adaptations of Sahara Desert Animals
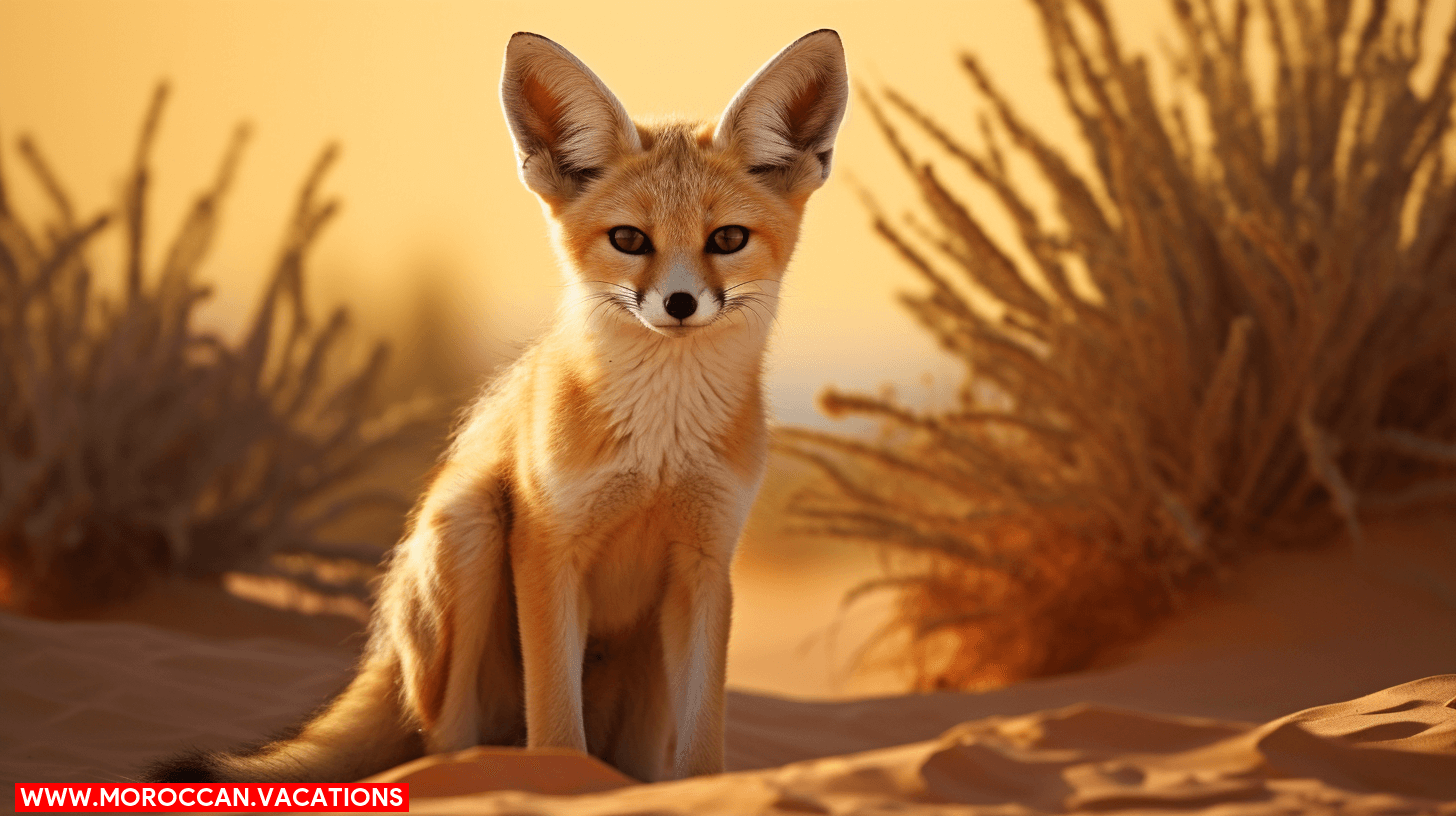


You’ll find that animals in the Sahara Desert have evolved sophisticated survival strategies to cope with extreme aridity. They exhibit specialized behaviors for water conservation, such as nocturnal activity patterns and highly efficient kidney functions. Additionally, physiological adaptations allow them to thrive in hot desert sands, which include unique heat exchange mechanisms and sand-swimming abilities.
Survival Strategies in Extreme Arid Conditions
Many animals in the Sahara Desert have evolved specialized adaptations to thrive in its harsh climate. You’ll find creatures with remarkable traits that underscore their freedom to live in a place where many others cannot survive. Each species has honed its strategies, leveraging the sparse resources to their advantage. Consider these key survival tactics:
- Desert vegetation reliance: Some species have adapted to extract the maximum nutrients from limited plant life.
- Nocturnal activity patterns: Animals avoid the scorching daytime heat by being active at night.
- Sand dune navigation: Exceptional skills in traversing the ever-shifting dunes are a must.
- Extreme temperature endurance and subterranean moisture access: Survival often hinges on an animal’s ability to withstand temperature extremes and tap into hidden water sources.
In these ways, desert dwellers exhibit a profound resilience and an intricate understanding of their environment.
Specialized Behaviors for Water Conservation
How do Sahara Desert animals conserve water with their unique behaviors? They’ve honed specialized adaptations that are as meticulous as they are vital. Nocturnal activity cycles allow creatures to avoid the scorching daytime temperatures, significantly reducing the need for water. Many species have also developed sophisticated burrowing techniques, creating subterranean havens that preserve moisture and maintain lower temperatures.
Furthermore, their physiology has adapted to maximize metabolic water production, extracting every possible drop from the food they consume. This internal water generation is a critical adaptation in an environment where liquid water is scarce. Expertly navigating the vast sand dunes, these animals locate and utilize sparse desert plant adaptations, which themselves are experts at water storage. Each behavior is a testament to the animals’ relentless pursuit of conservation in the face of relentless aridity.
Adaptations for Living in Hot Desert Sand
Beyond their water-saving behaviors, the Sahara’s animals exhibit remarkable physical traits that enable them to thrive on its hot sands. Their adaptations have evolved over millennia, granting them the freedom to roam an environment that seems harsh and unforgiving to the unadapted eye. These include:
- Desert vegetation camouflage: Animals blend seamlessly with their surroundings, evading predators and sneaking up on prey.
- Nocturnal activity cycles: Most desert dwellers switch to night-time activity to avoid the scorching daytime heat.
- Sand swimming techniques: Certain species, like the sandfish skink, move through sand as if it were water, a method that conserves energy and shields from solar radiation.
- Evaporative cooling behaviors: Some animals utilize the principle of evaporative cooling to regulate body temperature, despite scarce water sources.
Predator-Prey Relationships in the Sahara Ecosystem
In the Sahara’s intricate ecosystem, you’ll find predators and prey engaged in a perpetual dance of survival, each employing exceptional adaptations to outwit the other. Desert carnivores, such as the swift-footed cheetah and the cunning sand fox, have honed their nocturnal hunting techniques to conserve energy and exploit the cooler nighttime temperatures. Waterhole dynamics play a critical role as these scarce resources become stages for ambushes by thirsty predators. Prey species, meanwhile, exhibit dietary adaptations, consuming moisture-rich plants or burrowing deep to avoid the heat and detection. Scavenger survival is a testament to the efficiency of the Sahara’s food web, with opportunists like the vulture adeptly locating carcasses before they are reclaimed by the unforgiving sun.
Role of Hibernation and Burrow Digging in Desert Animal Survival
Considering the extreme conditions of the Sahara, you’ll find animals like the fat-tailed gerbil employing hibernation and burrow digging as crucial survival strategies. These behaviors are not just random acts of desperation, but rather finely tuned adaptations that ensure survival in one of the harshest environments on Earth.
- Desert Estivation: Some species enter a dormant state during extreme heat to conserve energy.
- Nocturnal Activity: Limiting movement to nighttime hours avoids the lethal daytime temperatures.
- Temperature Regulation: Burrows maintain a more stable temperature, providing a refuge from the harsh climate.
- Sand Swimming: Certain animals move through the sand to escape solar radiation and predators.
These strategies are indispensable for maintaining bodily functions within viable limits, allowing these creatures the freedom to thrive despite the oppressive desert conditions.
Conservation Efforts for Sahara Desert Animal Species
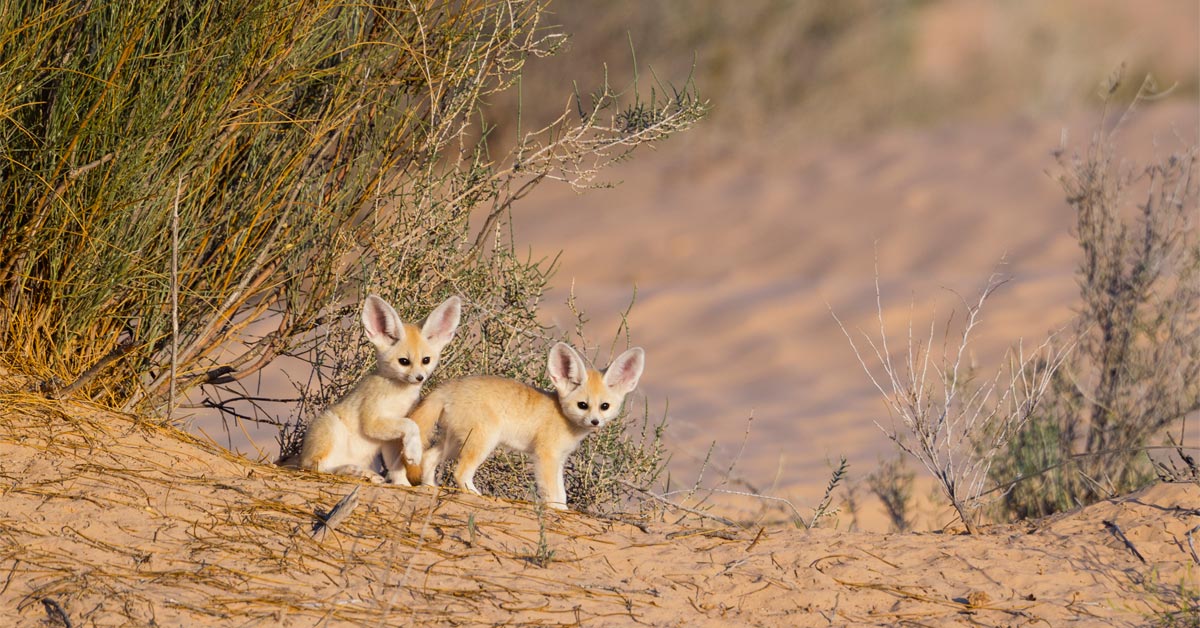


Photo by: @https://www.earthtouchnews.com/conservation/conservation/spirit-of-the-sahara/
You’ll find that conservation efforts for Sahara Desert animal species are critical due to the pressures of climate change, poaching, and habitat loss. These initiatives focus on protecting endangered species, preserving their natural habitats, and maintaining sustainable food sources. Identifying successful strategies hinges on analyzing challenges, bolstering community involvement, and learning from established conservation success stories.
Initiatives to Protect Endangered Sahara Desert Animals
Many of the unique animals you find in the Sahara Desert are the focus of international conservation efforts aimed at preventing their extinction. These initiatives are methodically tackling the challenges faced by these species, including:
- Desert poaching issues: Strengthening anti-poaching patrols and legal frameworks.
- Water resource management: Developing sustainable practices to ensure animals have access to life-sustaining water.
- International protection agreements: Collaborating across borders to create sanctuaries and protected areas.
- Climate change effects: Researching the impact and developing strategies to mitigate harm to desert ecosystems.
Your understanding of these efforts is crucial, as they are not just about saving animals—it’s also about preserving the freedom of nature against the encroachment of human-caused threats like climate change and renewable energy impacts.
Preservation of Natural Habitats and Food Sources
Building on these conservation efforts, you also play a vital role in preserving the Sahara Desert’s natural habitats and food sources, which are indispensable for the survival of its unique wildlife. In the face of desertification threats and water scarcity, it’s crucial to analyze the impact of human activities on these fragile ecosystems. Habitat fragmentation and climate change effects further exacerbate the challenges faced by native species.
| Threat | Consequence | Conservation Measure |
| Desertification | Loss of biodiversity | Sustainable land management |
| Water Scarcity | Compromised survival of species | Creation of artificial water sources |
| Habitat Fragmentation | Increased vulnerability to predators | Protected area expansion |
| Illegal Wildlife Trade | Species population depletion | Enforcement of anti-poaching laws |
Methodical conservation strategies are essential to combat illegal wildlife trade and ensure freedom for the Sahara’s inhabitants. Your awareness and involvement are key to these creatures’ continued existence.
Challenges in Sustainable Wildlife Conservation in the Sahara
Despite your best efforts, maintaining wildlife conservation in the Sahara faces multifaceted challenges that threaten the delicate balance of this arid ecosystem. The desert’s vastness and harsh conditions demand a strategic, freedom-centric approach, empowering both wildlife and people. To understand the scope, consider these critical issues:
- Desertification impacts: Expanding deserts shrink habitable zones, stressing animal populations.
- Water scarcity: Essential for all life, dwindling water sources intensify survival struggles.
- Illegal wildlife trade: It undermines conservation, robbing species of their freedom and future.
- Climate change effects: It exacerbates existing threats, demanding adaptive and resilient strategies.
Your role is pivotal. Encourage local community engagement, as their involvement is key to tailoring effective conservation measures that respect the freedom of both humans and wildlife in the Sahara.
Community Involvement and Awareness Programs
How can you, as a member of the global community, contribute to conservation efforts that protect the diverse animal species of the Sahara Desert? By adhering to desert tour guidelines, you ensure minimal disturbance to natural habitats. Engage in community eco projects that emphasize the importance of the ecosystem. Support local participation incentives, motivating indigenous stewardship of wildlife resources. Advocate for and involve yourself in environmental education campaigns to spread awareness on the fragility and significance of desert species. Participate or aid in establishing wildlife monitoring networks, providing essential data for better management strategies. Your methodical involvement can lead to a well-informed public, eager to safeguard the Sahara’s fauna. Through these meticulous actions, you champion the cause for freedom, not only for yourself but for all life in the desert.
Success Stories in Sahara Desert Animal Conservation
Your efforts in supporting Sahara Desert conservation have contributed to several triumphs in the protection of its unique wildlife. The analytical examination of these successes reveals a detailed tapestry of interlinked strategies:
- Desertification impact: Initiatives to combat land degradation have seen local species thrive in stabilizing ecosystems.
- Water scarcity solutions: Ingenious conservation methods ensure life-sustaining resources reach flora and fauna, mitigating drought stress.
- Illegal wildlife trade: Vigilant enforcement and community education have reduced poaching, giving vulnerable species a chance to rebound.
- Climate change effects: Investment in renewable energy installations minimizes habitat disruption, providing a buffer against the harsh realities of climate alteration.
In this pursuit of freedom for Sahara’s wildlife, each step you take ushers in hope for a sustainable coexistence with nature’s resilient inhabitants.
Importance of Sahara Desert Animals in the Ecosystem
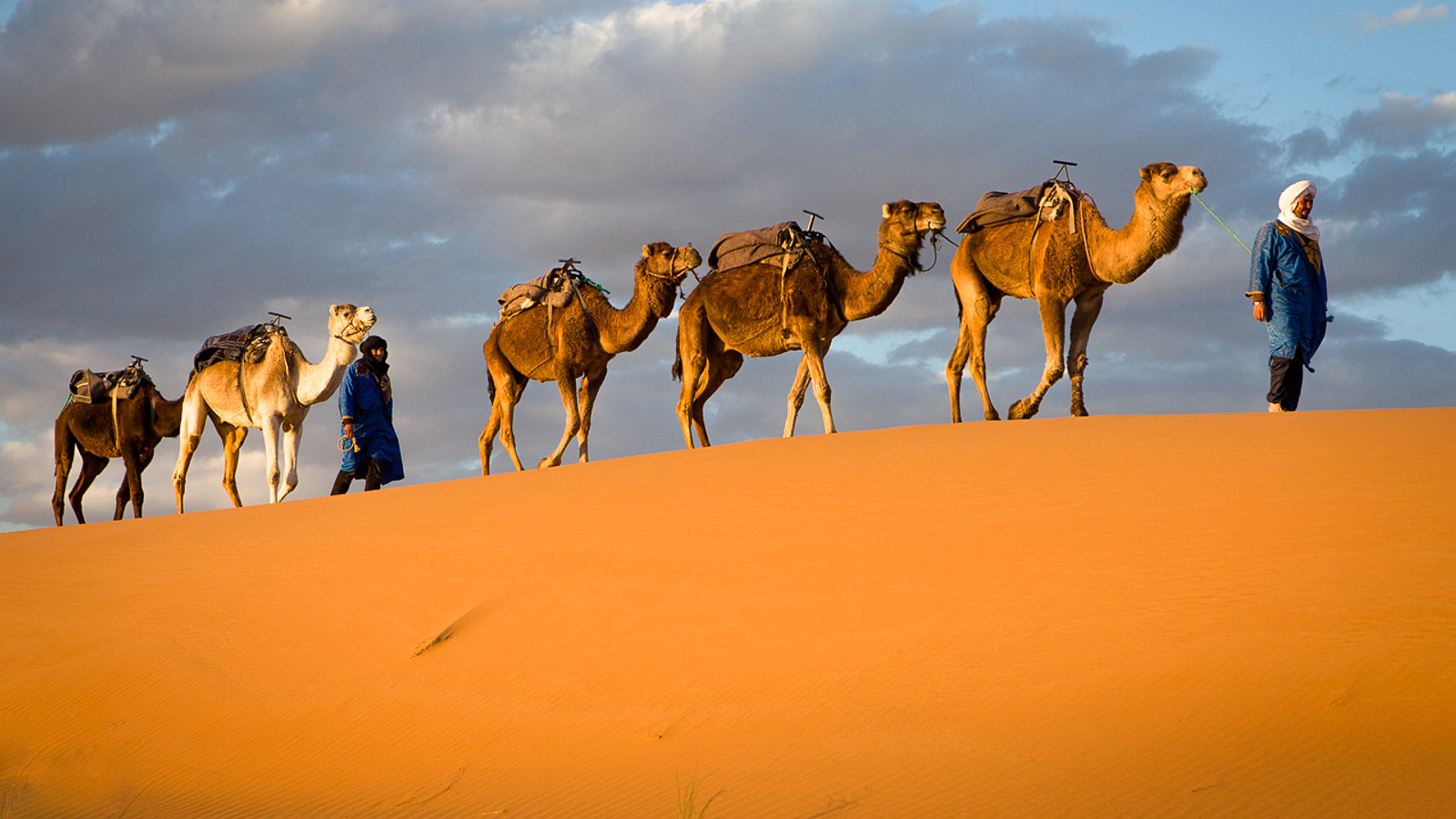


Photo by: @https://www.worldhistory.org/article/1344/the-camel-caravans-of-the-ancient-sahara/
You’ll find that animals in the Sahara Desert play crucial roles in maintaining the ecosystem’s health, such as pollination and seed dispersal, which ensure the survival of plant species. They also contribute to soil health and aid in microclimate regulation, processes that are essential for the harsh desert environment. Furthermore, the migration patterns of these animals are instrumental in maintaining the ecological balance, highlighting the interconnectedness of life in this vast arid region.
Role of Sahara Desert Animals in Pollination and Seed Dispersal
Why should you consider the creatures of the Sahara as crucial players in the desert’s ecosystem, particularly in pollination and seed dispersal? The Sahara’s harsh environment has led to remarkable adaptations among its wildlife, ensuring the continuation of plant species that are vital to the desert’s health.
- Desert bee species: These specialized pollinators have adapted to the extreme conditions and are essential for flowering plants’ reproduction.
- Nocturnal pollinators: Creatures like bats and moths avoid the heat, serving as vital nighttime pollinators for various plant species.
- Flowering cactus adaptation: Cacti have evolved alongside pollinators, resulting in mutualistic relationships crucial for survival.
- Wind dispersal mechanisms: In the absence of abundant wildlife, some plants have developed wind dispersal techniques to spread their seeds, showcasing the diverse strategies of Sahara flora.
This intricate web of interactions, including insect-plant coevolution, highlights the freedom and resilience of life in the desert ecosystem.
Contribution to Soil Health and Microclimate Regulation
Beyond pollination and seed dispersal, the fauna of the Sahara play a pivotal role in maintaining soil health and regulating the microclimate essential for sustaining desert life. These animals are critical in mitigating desertification effects by participating in nutrient cycling and soil stabilization. Your understanding of their importance should be both methodical and comprehensive.
| Factor | Contribution |
| Microbial Biodiversity | Diverse animal excretions bolster microbial populations, which in turn enhance soil structure and fertility. |
| Nutrient Cycling | Faunal activities, such as foraging and burrowing, accelerate the breakdown of organic matter, enriching the soil with essential nutrients. |
| Soil Stabilization | Movement and dwelling habits of desert species contribute to compacting and binding the soil, reducing erosion and aiding in moisture retention. |
Each creature’s existence contributes significantly to organic matter contributions, ensuring a balanced ecosystem where freedom to thrive is paramount.
Impact of Animal Migration Patterns on Ecological Balance
As you explore the Sahara, it’s crucial to understand how the migration patterns of its animals are fundamental to the ecological equilibrium of this vast desert. Animal movements impact the environment in several ways:
- Desertification effects: Migratory species help mitigate desertification by dispersing seeds and maintaining the diversity of flora.
- Water source competition: Seasonal migrations alleviate the pressure on water sources, ensuring shared access among wildlife.
- Climate change impact: Migration patterns reflect the adaptability of species to the evolving climate, influencing the desert ecosystem’s resilience.
- Transboundary wildlife corridors: Maintaining these routes is essential for species survival, necessitating international conservation collaboration to safeguard freedom of movement across borders.
Analyzing these factors sheds light on the intricate balance within the Sahara, emphasizing the freedom nature requires to thrive.
Relationship Between Desert Animals and Indigenous Plant Species
In the heart of the Sahara, you’ll find a reciprocal relationship between native animals and indigenous plants, each relying on the other for survival and sustenance. Desert vegetation adaptations have evolved to overcome harsh conditions—deep-rooted systems that tap into scarce water reserves and thickened leaves minimizing water loss. These plant survival strategies are critical in a landscape where photosynthesis challenges—like extreme heat and intense sunlight—prevail. Animals, in turn, depend on these hardy plants for nourishment and shelter amidst soil nutrient scarcity.
Symbiotic relationships flourish: plants provide food while animals facilitate pollination and seed dispersal, ensuring species propagation. It’s a meticulously balanced ecosystem, where each organism’s freedom to thrive hinges on the interconnected survival of others.
Interdependence of Predators and Prey in the Sahara Desert Food Chain
You’ll discover that numerous animals, from tiny insects to majestic predators, form a complex web of interdependence in the Sahara’s ecosystem. The survival dance between these creatures is marked by:
- Predator camouflage techniques, allowing hunters like the sand vipers to blend seamlessly with their environment.
- Nocturnal hunting strategies, employed by predators such as the fennec fox to capitalize on cooler temperatures and unsuspecting prey.
- Scavenger dynamics, where animals like the desert hyena clean up the remains, ensuring nutrient recycling within the habitat.
- Prey escape mechanisms, demonstrating how gazelles and other nimble creatures evade capture, maintaining a delicate balance.
This intricate network of life underscores not just interspecies competition but also the collective pursuit of freedom and survival amidst the harsh desert climes.
Human Interaction and Cultural Significance of Sahara Desert Animals
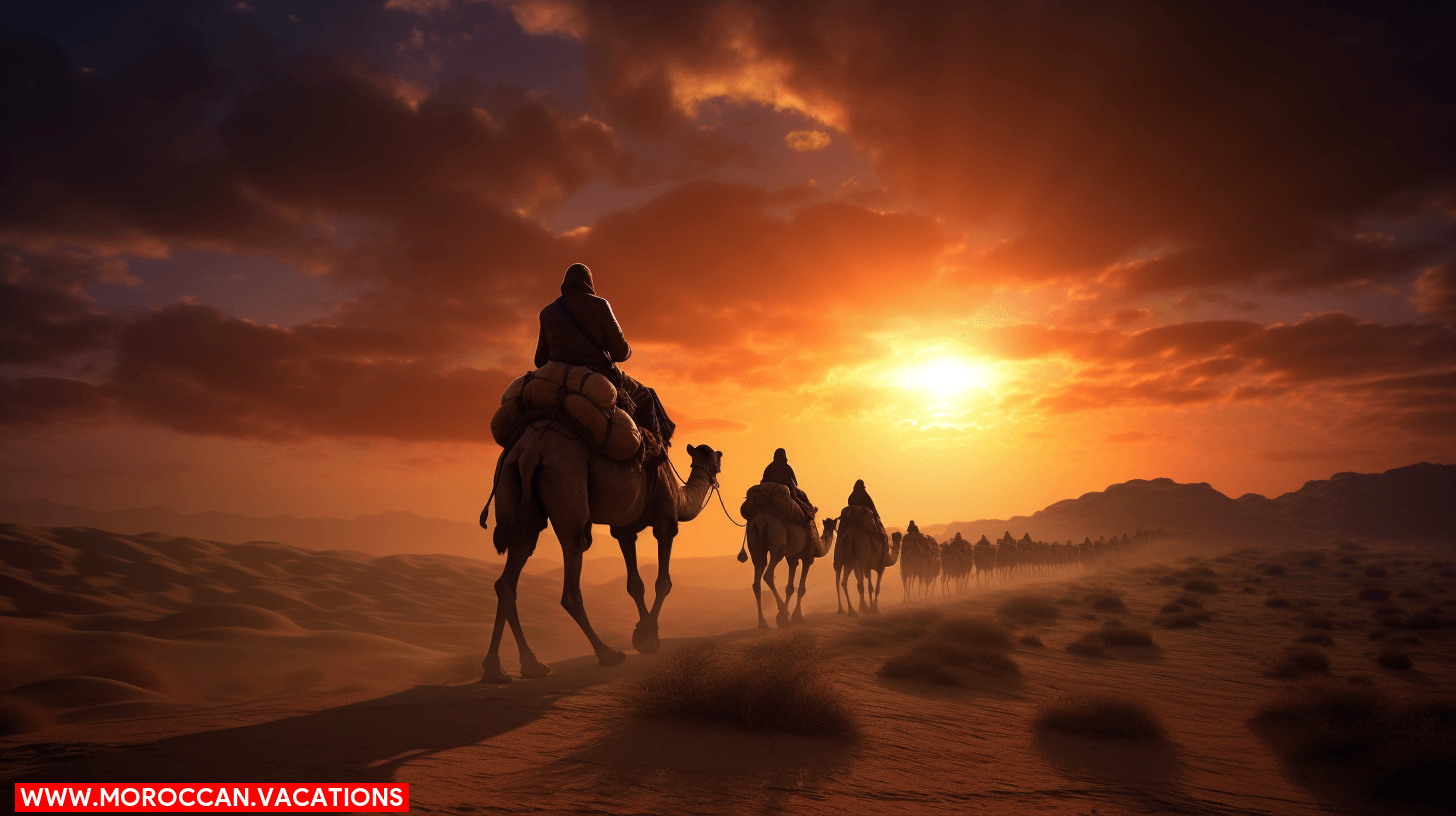

As you explore the Sahara Desert’s wildlife, you’ll find that animals have historically been integral to the survival of indigenous tribes, providing essential resources and shaping cultural narratives. The animals’ portrayals in folklore and art often carry symbolic meanings, reflecting the profound connection between humans and nature in this harsh environment. Today, balancing the sustainable use of desert wildlife with conservation efforts poses a complex challenge, necessitating careful analysis of ecotourism impacts and the role of scientific research in preserving these species.
Historical Utilization of Desert Animals by Indigenous Tribes
Throughout history, indigenous tribes have relied on a variety of Sahara Desert animals for their survival and cultural practices. You’ll find that their knowledge, deeply embedded in tradition and necessity, has shaped a unique symbiosis with these desert inhabitants. Here’s an analytical glimpse into their world:
- Desert animal myths that have shaped tribal belief systems and decision-making
- Traditional hunting techniques, honed over centuries, for sustainable living
- Indigenous animal uses, from medicinal remedies to crafting materials
- Tribal conservation wisdom, ensuring species protection and ecological balance
Symbolic Representations of Sahara Desert Animals in Folklore and Art
Discover how animals of the Sahara Desert hold profound symbolic meaning in local folklore and art, reflecting your deep-seated cultural connections to this arid landscape. Desert iconography is rich with artistic motifs derived from the endurance and adaptability of these creatures. Each species carries a narrative, woven into the very fabric of tradition. The folklore origins of these tales often date back centuries, where they have shaped cultural symbols that continue to resonate within communities.
Mythological creatures, born from the fusion of reality and imagination, are emblazoned in the collective memory, serving as emblems of freedom and survival. Every depiction is a meticulous tribute to the intricate bond between humans and the natural world, encapsulating a respect for the sovereignty inherent in the wild.
Modern-Day Challenges and Opportunities in Sustainable Use of Desert Wildlife
You’ll encounter both challenges and opportunities when aiming to sustainably manage the wildlife that calls the Sahara Desert home, a task deeply intertwined with cultural heritage and the survival of these species. Consider the following:
- Desertification impacts: Degradation of habitats threatens species, requiring innovative conservation strategies.
- Climate change effects: Adapting to shifting ecosystems is critical for the resilience of desert fauna.
- Illegal wildlife trade: Enforcement of laws and community engagement are key to protecting endangered species.
- Renewable energy projects: Balancing development with wildlife preservation, especially in water resource management, offers a sustainable path forward.
Analyzing these elements demands a methodical approach, dissecting each challenge and opportunity with precision, ensuring that your actions contribute to the freedom and flourishing of Sahara’s wildlife legacy.
Ecotourism and Educational Conservation Programs Involving Sahara Desert Animals
As you venture into the Sahara, engaging in ecotourism and educational conservation programs offers a direct route to appreciating and safeguarding the desert’s unique wildlife. Delving into desert safari experiences, you’ll find that sustainable tourism practices are critical. You’re empowered to make choices that minimize your footprint, such as adhering to eco-friendly travel tips like using solar-powered equipment or reducing water waste. It’s vital to recognize the climate change impacts on Sahara’s ecosystem, understanding how rising temperatures and shifting weather patterns affect its inhabitants. In this context, wildlife photography ethics become more than guidelines; they’re a commitment to responsible interaction with fauna. By participating in these programs, you contribute to a global movement that values freedom, both for yourself and the wildlife calling the Sahara home.
Role of Research and Scientific Studies in Sahara Desert Animal Preservation
While you explore the Sahara, it’s essential to understand how research and scientific studies contribute to the preservation of its unique animal life, which holds a profound place in local cultures and human history. The analytical rigor applied to:
- Desert research methodologies
- Habitat mapping techniques
- Understanding climate change effects
- International collaboration importance
ensures a detailed approach to conserving biodiversity. Methodical habitat mapping pinpoints where protection is crucial, while desert research methodologies adapt to the challenging environment. Analyzing scientific data reveals the stark realities of climate change effects, guiding targeted actions. The freedom to thrive in their natural habitats is safeguarded by international collaboration, which is vital for pooling resources and knowledge. Your awareness of these efforts helps champion the cause for these creatures of the Sahara.
Introducing Ayoub Karbachi, a brilliant wordsmith and curator of the Moroccan Vacations website. Prepare to immerse yourself in mesmerizing narratives and extraordinary moments, as he unveils the allure of Morocco's captivating destinations like never before.
Related Articles
What to Wear in Morocco: Essential Tips for Dressing in The Kingdom
Discover essential tips for dressing in the Kingdom with our comprehensive guide on what to wear in Morocco. Navigate cultural nuances effortlessly and make a statement with your attire.
Where Is Sahara Desert?
Discover the fascinating whereabouts of the Sahara Desert with our comprehensive guide. Uncover its unique geography, wildlife, and cultural significance.
What Time Is It in Morocco?
Discover the enchanting experience of time in Morocco with our comprehensive guide. Explore the rich cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and unique traditions that make every moment in Morocco truly unforgettable.



